Elements of Cannabis: Cannabinoids 101
Cannabis, like any medicinal plant, consists of various compounds that can interact with the human body when consumed or applied topically.
The main compounds of the Cannabis plant are phytocannabinoids, more commonly referred to as cannabinoids. Phytocannabinoids also occur in non-psychoactive plants such as echinacea purpura, a common alternative medicine, used as an immune booster, that is sold in health food stores across the country.
Each of the more than 113 cannabinoids within the cannabis genus has unique properties that cause different effects on your body and mind.
Within our bodies, we have a number of systems that handle different functions. Our digestive system processes what we consume to extract nutrients and energy to feed our bodies. Our endocrine system is made up of glands that produce hormones to regulate metabolism, growth and development, sexual function, reproduction, sleep, and mood.
We also have an Endogenous Cannabinoid or Endocannabinoid System (ECS) that works to establish and maintain our health. This system was first discovered in 1992 and is considered by a growing number of scientists to be the most important system in our bodies.
Our internal system contains endocannabinoids that in turn have receptors. These receptors are embedded in our cells and are present in our brain, organs, glands, connective tissues, and immune cells. Our Encannabinoid System performs different tasks depending on where it is functioning, but essentially endocannabinoids work to bring our internal systems into balance. The technical term for this is “homeostasis.”
So far, researchers have identified two cannabinoid receptors: CB1 that is mostly in our nervous system, connective tissues, glands, and organs; and CB2 that is in our immune system. Many tissues within our bodies contain both CB1 and CB2 receptors. Researchers also think there may be a third cannabinoid receptor yet to be discovered.
Our Encannabinoid System performs different tasks depending on where it is functioning, but essentially endocannabinoids work to bring our internal systems into balance.
So how does cannabis affect our bodies through our endocannabinoid system?
You’ve probably heard of THC (Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol). THC is the cannabinoid with psychoactive effects, meaning that it interacts with the your brain to produce a variety of reactions ranging from relaxation to euphoria.
Other cannabinoids in cannabis include CBD (cannabidiol) and CBN (cannabinol). CBD is currently available legally in a variety of products (e.g. topicals and tinctures) derived from industrial hemp, the sister and non-intoxicating plant related to cannabis. CBN is the compound in cannabis that causes drowsiness.
Familiarizing yourself with the primary cannabinoids and their effects can help you find the right strains. With the right ratio of THC to other cannabinoids, cannabis may help reduce inflammation, relieve pain, ease insomnia and provide other health and wellness benefits.
Additional Reading
Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System [Ethan Russo, MD Medical Director, PHYTECS]
Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System [NORML]
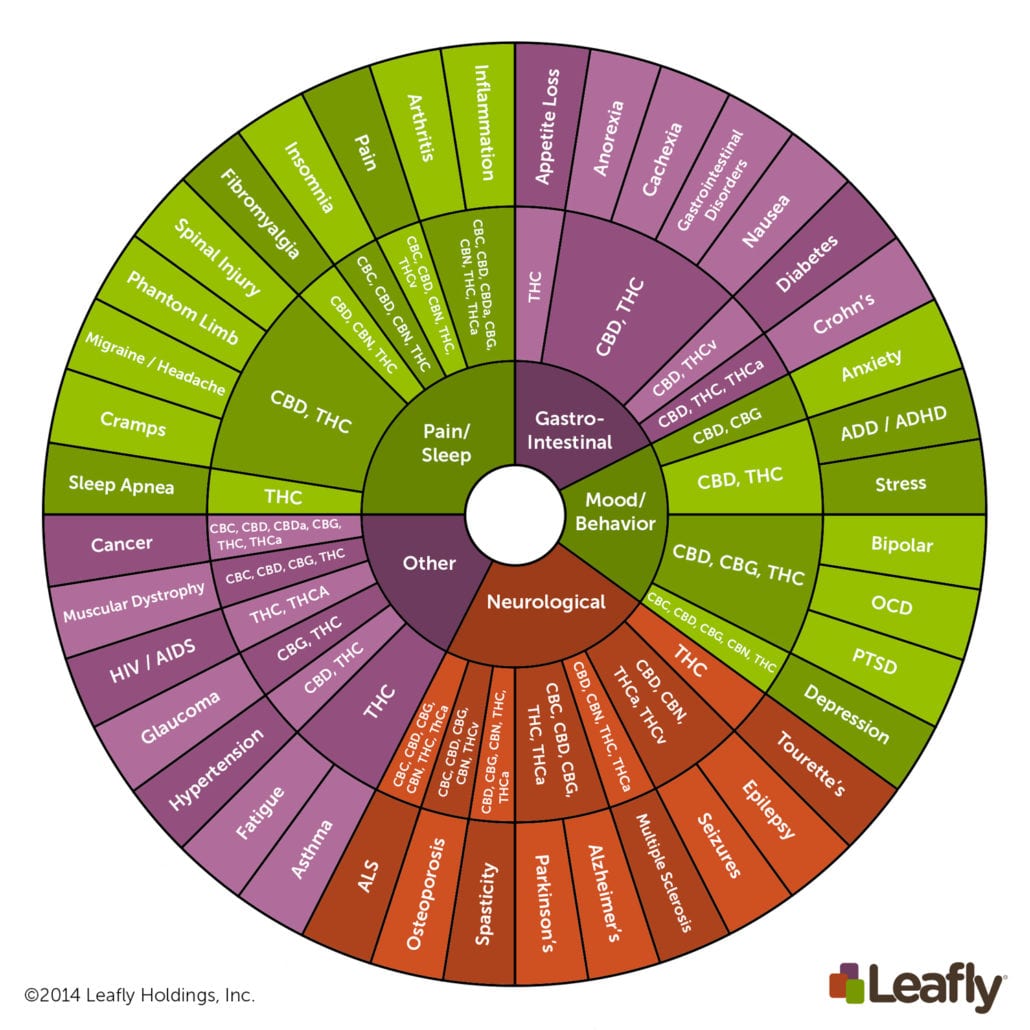
Here’s a helpful illustration from Leafly of cannabinoids contained in cannabis and their potential benefits.










Trackbacks & Pingbacks
[…] Cannabinoids found in cannabis, such as Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD), have been shown to interact with the ECS in a way that has been described as neuroprotective as well as antiinflammatory and supportive of immune response. Because of the way THC and CBD interact with one another, cannabis physicians often recommend full-spectrum CBD products or THC products with some CBD to improve the therapeutic effects. CBD can help temper the intoxicating effects of THC while THC can enhance or complement the anti-anxiety and anti-inflammatory effects of CBD. […]
[…] CBD extracted fully from the plant and separating it from all other chemical compounds, including cannabinoids, is called an “isolate.” This isolated CBD is tasteless and odorless and can be added to other […]
[…] release the active elements of cannabis such as the cannabinoids or terpenes, you need to heat up the plant material. Rather than using the buds of the cannabis […]
[…] and its cannabinoids and terpenes can positively affect the ECS, bringing it into homeostasis or balance. When our […]
[…] feeling comfortable enough to be intimate with a partner, and even impact your ability to orgasm. Cannabinoids can be effective in managing and mitigating […]
[…] Gatherings for women in cities around the world is to empower more women with knowledge about the Endocannabinoid System and why cannabis is so compatible with the human […]
[…] Don’t know what cannabinoids are? Check out this post! […]
[…] feeling comfortable enough to be intimate with a partner, and even impact your ability to orgasm. Cannabinoids can be effective in managing and mitigating […]
[…] of the elements in cannabis include Cannabinoids as well as Terpenes. Terpenes are naturally occurring elements found in not only cannabis but a […]
Comments are closed.